Transfinger Piercing and Septum: Difference between pages
(Created page with "<html><div class="mw-content-ltr" dir="ltr" id="mw-content-text" lang="en"><p>In many ways, the pad of a finger is similar to an earlobe — essentially just skin covering some fatty filler tissue. In most of the finger this is complicated by nerves and tendons, but in the final joint, not only is the bone recessed and thinner, but the tendons and other essential <i>"don't mess around near me"</i> anatomy is not as present, making a <b>transfinger piercing</b> more plaus...") |
(Page conversion via llm-mediawiki-rev -jwm) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Septumcbr.jpg|thumb|right|Captive bead ring worn in a septum piercing]] | |||
[[File:Halfinchseptum.jpg|thumb|right|1/2" septum]] | |||
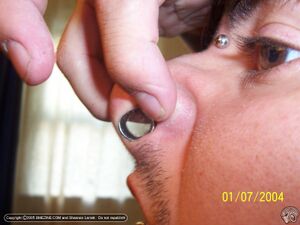
'''The septum piercing''' passes through the nasal septum (the middle of the nose) and is often referred to as a "bull-ring piercing." The nasal septum is the cartilaginous tissue dividing wall between the [[Nostrils]]. Generally, the cartilage itself is not pierced, but rather the small gap between the cartilage (also known as the "[[:Sweet spot (page does not exist)|sweet spot]]") and the bottom of the nose, typically at a [[Gauge]] no smaller than 14ga (1.6mm). | |||
It should be noted that extreme stretching of the septum will definitely deform the nose, pushing it down and out. This deformity is often referred to as "septum droop." The degree of deformity will differ from person to person depending on their nasal anatomy. | |||
==Contents== | |||
*1 [[#Placement|Placement]] | |||
*2 [[#Procedure|Procedure]] | |||
*3 [[#Healing and aftercare|Healing and aftercare]] | |||
*4 [[#Jewelry|Jewelry]] | |||
*5 [[#History and culture|History and culture]] | |||
*6 [[#See Also|See Also]] | |||
*7 [[#Related Risks|Related Risks]] | |||
==Placement== | |||
The septum piercing passes through the nasal septum (the middle of the nose). | |||
==Procedure== | |||
Septum piercings are normally performed like a standard needle piercing (sometimes using a [[Septum clamp]] to help), although [[Dermal punch]] may be used to create larger gauge piercings. Some advanced artists may also use a [[Scalpel]] to create or enlarge the piercing to accept much larger jewelry. | |||
==Healing and aftercare== | |||
The healing time on average is usually 1–3 months. Aftercare is usually [[Salt soaks]], 2 times a day. | |||
==Jewelry== | |||
[[File:Septumretainer.jpg|thumb|right|12 gauge retainer]] | |||
While [[Captive bead ring]] and [[Circular barbell]] are common jewelry, a piece of jewelry called a [[Septum retainer]] (which is staple shaped) can be worn flipped up inside the nostrils to completely hide the piercing. Septum piercings can come in all sizes ranging from 14g to 1", though 14ga is considered the minimum size. In larger sizes a "[[Septum keeper]]" or "[[:Bullet plug (page does not exist)|bullet plug]]" are both used for comfort. | |||
==History and culture== | |||
Septum piercings were popular among certain Native American peoples in history; the Shawnee leaders Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa, for example, had such piercings. Septum piercings are also sometimes performed on bulls as part of the process to break them for the farm. This process uses a hinged brass ring with sharpened ends to facilitate insertion. Afterwards, the open ends are held together by means of a screw. | |||
[[Paul King]] adds, | |||
:''[[New Guinea]] is perhaps most famous for septum piercings. The [[:Kangi (page does not exist)|Kangi]] of New Guinea pierce the septum using a bat bone and sweet potato. During the initiation, the face is blackened with charcoal. The hair on the head is plucked out, all but a tuft. This makes him safe from the magic of women and impervious to death and pain.'' | |||
:''Much tradition and myth is steeped into the Kiman-Papuans of South Irian Jaya. Progressive feasts are offered especially for the male children at stages in the process of loosening connections with their mother. At hair cutting and earlobe, nostril and nasal septum fests, holes are made to wear the ornaments that signify the growing boy's status as a man in the community—for example, the pig's bone through the septum shows that he is a headhunter, and the [[Blood]] that flows from the piercing is supposed to be womb blood that must be removed symbolically.'' | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Septum Funk]] | |||
*[[Funk]] | |||
*[[Nostril Piercing]] | |||
*[[Nasallang]] | |||
*[[Septril]] | |||
*[[Austin Bar]] | |||
==Related Risks== | |||
*[[Airbag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:14, 17 September 2023
The septum piercing passes through the nasal septum (the middle of the nose) and is often referred to as a "bull-ring piercing." The nasal septum is the cartilaginous tissue dividing wall between the Nostrils. Generally, the cartilage itself is not pierced, but rather the small gap between the cartilage (also known as the "sweet spot") and the bottom of the nose, typically at a Gauge no smaller than 14ga (1.6mm).
It should be noted that extreme stretching of the septum will definitely deform the nose, pushing it down and out. This deformity is often referred to as "septum droop." The degree of deformity will differ from person to person depending on their nasal anatomy.
Contents
- 1 Placement
- 2 Procedure
- 3 Healing and aftercare
- 4 Jewelry
- 5 History and culture
- 6 See Also
- 7 Related Risks
Placement
The septum piercing passes through the nasal septum (the middle of the nose).
Procedure
Septum piercings are normally performed like a standard needle piercing (sometimes using a Septum clamp to help), although Dermal punch may be used to create larger gauge piercings. Some advanced artists may also use a Scalpel to create or enlarge the piercing to accept much larger jewelry.
Healing and aftercare
The healing time on average is usually 1–3 months. Aftercare is usually Salt soaks, 2 times a day.
Jewelry
While Captive bead ring and Circular barbell are common jewelry, a piece of jewelry called a Septum retainer (which is staple shaped) can be worn flipped up inside the nostrils to completely hide the piercing. Septum piercings can come in all sizes ranging from 14g to 1", though 14ga is considered the minimum size. In larger sizes a "Septum keeper" or "bullet plug" are both used for comfort.
History and culture
Septum piercings were popular among certain Native American peoples in history; the Shawnee leaders Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa, for example, had such piercings. Septum piercings are also sometimes performed on bulls as part of the process to break them for the farm. This process uses a hinged brass ring with sharpened ends to facilitate insertion. Afterwards, the open ends are held together by means of a screw.
Paul King adds,
- New Guinea is perhaps most famous for septum piercings. The Kangi of New Guinea pierce the septum using a bat bone and sweet potato. During the initiation, the face is blackened with charcoal. The hair on the head is plucked out, all but a tuft. This makes him safe from the magic of women and impervious to death and pain.
- Much tradition and myth is steeped into the Kiman-Papuans of South Irian Jaya. Progressive feasts are offered especially for the male children at stages in the process of loosening connections with their mother. At hair cutting and earlobe, nostril and nasal septum fests, holes are made to wear the ornaments that signify the growing boy's status as a man in the community—for example, the pig's bone through the septum shows that he is a headhunter, and the Blood that flows from the piercing is supposed to be womb blood that must be removed symbolically.