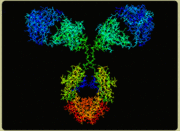Antibodies
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
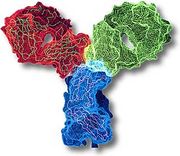
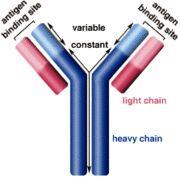
An antibody is a type of protein used by the body to help ward off bacteria, viruses and toxins the body recognizes as "bad." They are released by immune system cells known as plasma cells, and are keyed to a single type of pathogen. When an antibody encounters a pathogen of the correct type it attaches to it and serves as a marker, so that phagocytes can find and remove the offending substance.