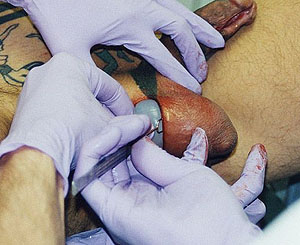
Scrotal Implant
Scrotal implants are beads or objects implanted inside the scrotum, typically either to replace missing testicles, or to enhance the appearance of the scrotum with larger balls.
A small number of doctors use "cupped" implants which actually form a sheath around the testicles, but most doctors prefer to implant a second, larger set of testicles beneath the real ones in the interest of safety.
Contents |
Materials
Silicone testicles (Neuticles) are sometimes used, especially when a natural testicle appearance is desired after castration. Implants can be made from stainless steel, titanium, PTFE, silicone, or other implant-grade materials.
Neuticles and products like them are sold through medical and veterinary suppliers and are not usually available to the general public (and may be illegal in some areas). There is, of course, the option of approaching them as a "high-school science teacher" or an "artist," but ultimately such a path is probably illegal and could lead to secondary problems.
Beads suitable for implantation, including larger beads, are available through most body jewelry manufacturers (just ask them for polished, undrilled beads in your desired size and material). They can also be obtained from industrial suppliers at a much lower cost, but they'd need to be properly finished before use.
Finally, note that medical-grade materials, especially in larger items (beads larger than 3/4" in diameter, for example) can get expensive. They're expensive for a reason, and if you skimp on materials, odds are you will regret it later. If your supplier, doctor, or artist cannot tell you exactly what is being put in you, you're not dealing with reputable people.
Procedure
Assuming that sterility requirements can be met, on a technical level, the procedure is no more difficult than many of the implant procedures attempted by amateur practitioners (who can be contacted through the obvious underground channels).
It is strongly urged that you seek the assistance of a trained and qualified medical professional for procedures such as this. Yes, it will cost more, and yes, it will mean having to answer more personal questions, but ask yourself: "How much is my life worth to me?"
Longterm Health Issues
The largest risk is infection, primarily in the time period immediately following the procedure. Bacteria trapped inside the scrotum can quickly grow to become a life-threatening infection literally overnight. Additionally, in cases where heavier implants (for example, things like 2" steel balls) are used, tissue death surrounding (especially below) the implant has been reported, leading to scrotal amputation after gangrene set in. If untreated, gangrene will spread and infect adjacent tissues. This may result in loss of other structures, including the testes, penis and lower limbs.
Using proper medical-grade materials is essential. If proper grade materials are not used, infection risks skyrocket, and at a minimum, various inflammatory responses can be expected. Implantation of unsuitable materials should not even be considered.
Legality
Laws vary from region to region, but, realistically, one must be an accredited medical doctor to legally perform such a procedure.