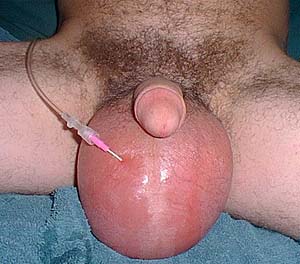
Saline injection
Inflation of the scrotum and other bits via saline solution
Saline solution (sterile 0.9% salt water) can be used to "inflate" body parts -- most commonly, this is the scrotum since, at least in part, it is the easiest to inflate. The penis shaft and breasts (in both men and women) can also be inflated. The saline solution can take a few days to reabsorb.
Caution must be taken to ensure that both the saline and the drip tubes and needles are sterile -- if not, a potentially life-threatening infection can easily be drawn inside the body.
Most commonly, the result is a gangrenous growth which, if it spreads is fatal. Gangrenous growths must be amputated to avoid metastasis. A gangrenous growth associated with genitalia can result in the loss of the genitals (both the testes and the penis) and, in extreme cases, the lower limbs.