Nipple: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "<html><div class="mw-content-ltr" dir="ltr" id="mw-content-text" lang="en"><p><br/> </p> <table style="text-align: right;"> <tr> <td style="width: 275px;"><a class="image" href="/index.php?title=File:Nipple-1.gif"><img alt="Nipple-1.gif" height="292" src="/images/5/52/Nipple-1.gif" width="266"/></a><br/> <p><i>Simplified breast and nipple anatomy:</i><br/> <b>1.</b> Fat<br/> <b>2.</b> Milk glands<br/> <b>3.</b> Areola<br/> <b>4.</b> Milk ducts<br/> <b...") |
(Page conversion via llm-mediawiki-rev -jwm) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| style="text-align: right;" | |||
|- | |||
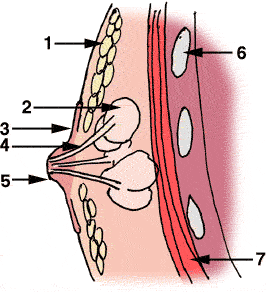
|style="width: 275px;" |[[File:Nipple-1.gif|thumb|Simplified breast and nipple anatomy:]] | |||
:''Simplified breast and nipple anatomy:'' | |||
# '''Fat''' | |||
# '''Milk glands''' | |||
# '''Areola''' | |||
# '''Milk ducts''' | |||
# '''Nipple''' | |||
# '''Ribcage and chest wall''' | |||
# '''Pectoral muscle''' | |||
|} | |||
The nipples are the protrusion on the chests of men and women, serving to deliver milk during lactation. This milk is made by glands behind and surrounding the nipple, although only about 1/3 of men have enough breast tissue (this condition is known as [[Gynecomastia|gynecomastia]]) to actually lactate (almost all women are able) — lactation is usually hormonally triggered, so [[Eunuch|eunuchs]] not taking [[Testosterone|testosterone]] may start to lactate. As a point of trivia, an excess of male hormones can destroy the breast tissue. These glands empty out of the nipple via the lactiferous ducts (milk ducts) and the areola (the surrounding pigmented area) also secretes a fluid to protect the nipple. If the milk ducts are blocked by scarring from a piercing, infections can be trapped inside, resulting in [[Mastitis|mastitis]]. | |||
Nipples are also sexual organs in both men and women, and in most people's become erect when stimulated (or cold). This happens due to a contraction of muscles covering the nipple. | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Third Nipple]] | |||
* [[Nipple Piercing]] | |||
* [[Nipple Stretching]] | |||
* [[Nipple Splitting]] | |||
* [[Nipple Removal]] | |||
* [[Inverted Nipples]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:41, 17 September 2023
|
The nipples are the protrusion on the chests of men and women, serving to deliver milk during lactation. This milk is made by glands behind and surrounding the nipple, although only about 1/3 of men have enough breast tissue (this condition is known as gynecomastia) to actually lactate (almost all women are able) — lactation is usually hormonally triggered, so eunuchs not taking testosterone may start to lactate. As a point of trivia, an excess of male hormones can destroy the breast tissue. These glands empty out of the nipple via the lactiferous ducts (milk ducts) and the areola (the surrounding pigmented area) also secretes a fluid to protect the nipple. If the milk ducts are blocked by scarring from a piercing, infections can be trapped inside, resulting in mastitis.
Nipples are also sexual organs in both men and women, and in most people's become erect when stimulated (or cold). This happens due to a contraction of muscles covering the nipple.