Magnetic Implant: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "<html><div class="mw-content-ltr" dir="ltr" id="mw-content-text" lang="en"><div class="thumb tright"><div class="thumbinner" style="width:182px;"><a class="image" href="/index.php?title=File:Magneticimplantonshannonlarratt.jpg"><img alt="" class="thumbimage" height="135" src="/images/thumb/c/cf/Magneticimplantonshannonlarratt.jpg/180px-Magneticimplantonshannonlarratt.jpg" width="180"/></a> <div class="thumbcaption"><div class="magnify"><a class="internal" href="/index.ph...") |
(Page conversion via llm-mediawiki-rev -jwm) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
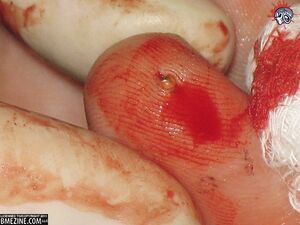
[[File:Magneticimplantonshannonlarratt.jpg|thumb|right|A magnetic implant, created by Jesse Jarrell and performed by Steve Haworth, on Shannon Larratt]] | |||
'''Magnetic implants''' have been used for several years in dentistry and reconstructive surgery, but their inclusion in the [[:Category:Body Modifications|body modification]] world has been quite a recent one. | |||
Having magnets [[:Category:Implants|implanted]] under the skin allows the wearer to attach magnetic items to the outside of the skin, and also enables the wearer to sense electromagnetic fields. | |||
[[:Samppa|Samppa]] implanted a few magnets in himself and close friends in the late 1990's, but they weren't very strong and were only capable of picking up small items. | |||
[[:Jesse_Jarrell|Jesse Jarrell]] and [[:Steve_Haworth|Steve Haworth]] decided to develop magnetic implants which were both smaller, and stronger, than those used by Samppa. The magnets used were neodymium iron boron alloy, with a thin gold plating, encapsulated in [[:Silicone|silicone]]. While most of the people who received these implants were satisfied with the post procedural result, many have gone on to develop problems with the implants which have necessitated their removal. The main problems have been caused by the rupturing of the silicone covering, bringing the metal into contact with bodily tissues, which in most cases caused it to rapidly break down. The most famously documented case of the failure of these implants was relating to those implanted in the fingers of [[:Shannon_Larratt|Shannon Larratt]]. His account of the problems leading to their removal can be found [http://www.bmezine.com/news/pubring/20060401.html here]. | |||
Steve and Jesse came out with a second generation of magnetic implant, which used injection-molded silicone rather than the dip-coating used in the first generation. This molding provided an even coat over the pill-shaped magnet, rather than bubble shape of the dip-coated magnet which lead to thin spots where the silicone was more likely to break down and cause failure. As such, the second generation magnets have not been subject to the same failures as the first generation ones were. Steve is now currently using a nickel-plated neodymium magnet which is 20% stronger than the gold-plated one. | |||
Magnetic implants have now been put into thousands of individuals, most of whom have had no problems. The only problems reported now are rejections which are the regular risk of any implant or piercing, as the body is naturally inclined to push them out if they do not encapsulate with scar tissue. | |||
== External Links == | |||
*[[:Implant_FAQ|Implant FAQ]] | |||
*[https://news.bme.com/2004/02/06/the-gift-of-magnetic-vision-the-publishers-ring/ The Gift of Magnetic Vision] | |||
*[https://news.bme.com/2006/01/15/magnetic-implants-a-six-month-retrospective-the-publishers-ring/ Magnetic Implants: A Six Month Retrospective] | |||
*[https://news.bme.com/2006/04/01/another-two-months-of-magnetic-implants-the-publishers-ring/ Another two months of magnetic implants] | |||
*[https://news.bme.com/wp-content/uploads/2008/09/pubring/guest/20060331.html Magnetic Implant Development and Updates] | |||
*[https://news.bme.com/2007/06/06/so-whats-it-like-having-magnetic-vision-bme-publishers-ring/ So what's it like having magnetic vision?] | |||
*[http://stevehaworth.com/magnetic-faq/ Steve Haworth's magnetic FAQ] | |||
*[https://www.wired.com/gadgets/mods/news/2006/06/71087 Wired - A Sixth Sense for a Wired World] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:31, 17 September 2023
Magnetic implants have been used for several years in dentistry and reconstructive surgery, but their inclusion in the body modification world has been quite a recent one.
Having magnets implanted under the skin allows the wearer to attach magnetic items to the outside of the skin, and also enables the wearer to sense electromagnetic fields.
Samppa implanted a few magnets in himself and close friends in the late 1990's, but they weren't very strong and were only capable of picking up small items.
Jesse Jarrell and Steve Haworth decided to develop magnetic implants which were both smaller, and stronger, than those used by Samppa. The magnets used were neodymium iron boron alloy, with a thin gold plating, encapsulated in silicone. While most of the people who received these implants were satisfied with the post procedural result, many have gone on to develop problems with the implants which have necessitated their removal. The main problems have been caused by the rupturing of the silicone covering, bringing the metal into contact with bodily tissues, which in most cases caused it to rapidly break down. The most famously documented case of the failure of these implants was relating to those implanted in the fingers of Shannon Larratt. His account of the problems leading to their removal can be found here.
Steve and Jesse came out with a second generation of magnetic implant, which used injection-molded silicone rather than the dip-coating used in the first generation. This molding provided an even coat over the pill-shaped magnet, rather than bubble shape of the dip-coated magnet which lead to thin spots where the silicone was more likely to break down and cause failure. As such, the second generation magnets have not been subject to the same failures as the first generation ones were. Steve is now currently using a nickel-plated neodymium magnet which is 20% stronger than the gold-plated one.
Magnetic implants have now been put into thousands of individuals, most of whom have had no problems. The only problems reported now are rejections which are the regular risk of any implant or piercing, as the body is naturally inclined to push them out if they do not encapsulate with scar tissue.