Scrotal Splitting and Scrotal removal: Difference between pages
(Page conversion via llm-mediawiki-rev -jwm) |
(Page conversion via llm-mediawiki-rev -jwm) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Scrotal | '''Scrotal removal''' and '''scrotal reduction''' is the surgical removal of all or part of the [[Scrotum|scrotum]]. It is not the same thing as [[Castration|castration]], but, in general, a scrotal removal is rarely done unless the individual is already a [[Eunuch|eunuch]] because an overly tight scrotum can be very uncomfortable. The procedure involves cutting off (generally with [[Scalpels|scalpels]] and [[Cautery tools|cautery tools]]) and then [[Suturing|suturing]] or [[Stapling|stapling]] the scrotum closed (although some people have successfully used an [[Elastrator|elastrator]] to do the scrotal removal post-castration). | ||
It should also be noted that scrotal removal and castration are not ''usually'' done at the same time. This is because castrations can swell '''a lot''', and if the scrotum is cut tightly, it is highly possible that the stitches may be torn out, resulting in the need for additional medical care. In almost every case of a [[Cutter|cutter]] being arrested for their work, this is what lead up to it. | |||
It is also important to note that a scrotal removal isn't just a matter of cutting off some extraneous skin like in an [[Earlobe removal|earlobe removal]]. The [[Scrotum|scrotum]] is highly vascular and muscular, and, in many individuals seeking scrotal removal, there can be dramatic scarring from previous procedures which can complicate the procedure. | |||
A | A small [[Scar|scar]] is usually left but scars are often virtually invisible in scrotal tissue. | ||
== | == Types of Scrotal Removal and Reduction == | ||
[[File:Scrotal_Removal_Diagram.jpg|right|200px|Scrotal Removal Diagram.jpg]] | |||
In the procedure below you can see the most common type of scrotal removal, the scrotum is shrunk by cutting off a portion of the lower end, discarding it, and suturing the remaining tissue back together. | |||
= | {| style="text-align: center;" | ||
|- | |||
| [[File:Scrotal_Removal-3.jpg|100px|thumb|Tissue marked for removal]] | |||
| [[File:Scrotal_Removal-4.jpg|100px|thumb|Excision of excess scrotum]] | |||
| [[File:Scrotal_Removal-5.jpg|100px|thumb|Note the anatomy!]] | |||
| [[File:Scrotal_Removal-6.jpg|100px|thumb|Stapled closed]] | |||
|} | |||
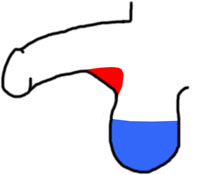
"Gooseneck" removals are also done, often by [[Cosmetic surgeons (page does not exist)|cosmetic surgeons]]. This is the removal of the scrotal skin that bridges between the scrotum itself and the lower shaft of the penis. In a [[DIY|DIY]] or [[Cutter|cutter]] context, this normally involves a [[Clamp and cut|clamp and cut]] procedure where a triangular section is removed. The remaining tissue is sutured back together giving the visual illusion of a longer penis. In the diagram on the right, the red tissue is what would be removed in a gooseneck reduction, and the blue tissue is what would be removed (more or less) in a standard scrotal reduction/removal such as the one illustrated in the procedural photos. | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Castration]] | |||
* [[Circumcision]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:07, 17 September 2023
Scrotal removal and scrotal reduction is the surgical removal of all or part of the scrotum. It is not the same thing as castration, but, in general, a scrotal removal is rarely done unless the individual is already a eunuch because an overly tight scrotum can be very uncomfortable. The procedure involves cutting off (generally with scalpels and cautery tools) and then suturing or stapling the scrotum closed (although some people have successfully used an elastrator to do the scrotal removal post-castration).
It should also be noted that scrotal removal and castration are not usually done at the same time. This is because castrations can swell a lot, and if the scrotum is cut tightly, it is highly possible that the stitches may be torn out, resulting in the need for additional medical care. In almost every case of a cutter being arrested for their work, this is what lead up to it.
It is also important to note that a scrotal removal isn't just a matter of cutting off some extraneous skin like in an earlobe removal. The scrotum is highly vascular and muscular, and, in many individuals seeking scrotal removal, there can be dramatic scarring from previous procedures which can complicate the procedure.
A small scar is usually left but scars are often virtually invisible in scrotal tissue.
Types of Scrotal Removal and Reduction
In the procedure below you can see the most common type of scrotal removal, the scrotum is shrunk by cutting off a portion of the lower end, discarding it, and suturing the remaining tissue back together.
"Gooseneck" removals are also done, often by cosmetic surgeons. This is the removal of the scrotal skin that bridges between the scrotum itself and the lower shaft of the penis. In a DIY or cutter context, this normally involves a clamp and cut procedure where a triangular section is removed. The remaining tissue is sutured back together giving the visual illusion of a longer penis. In the diagram on the right, the red tissue is what would be removed in a gooseneck reduction, and the blue tissue is what would be removed (more or less) in a standard scrotal reduction/removal such as the one illustrated in the procedural photos.